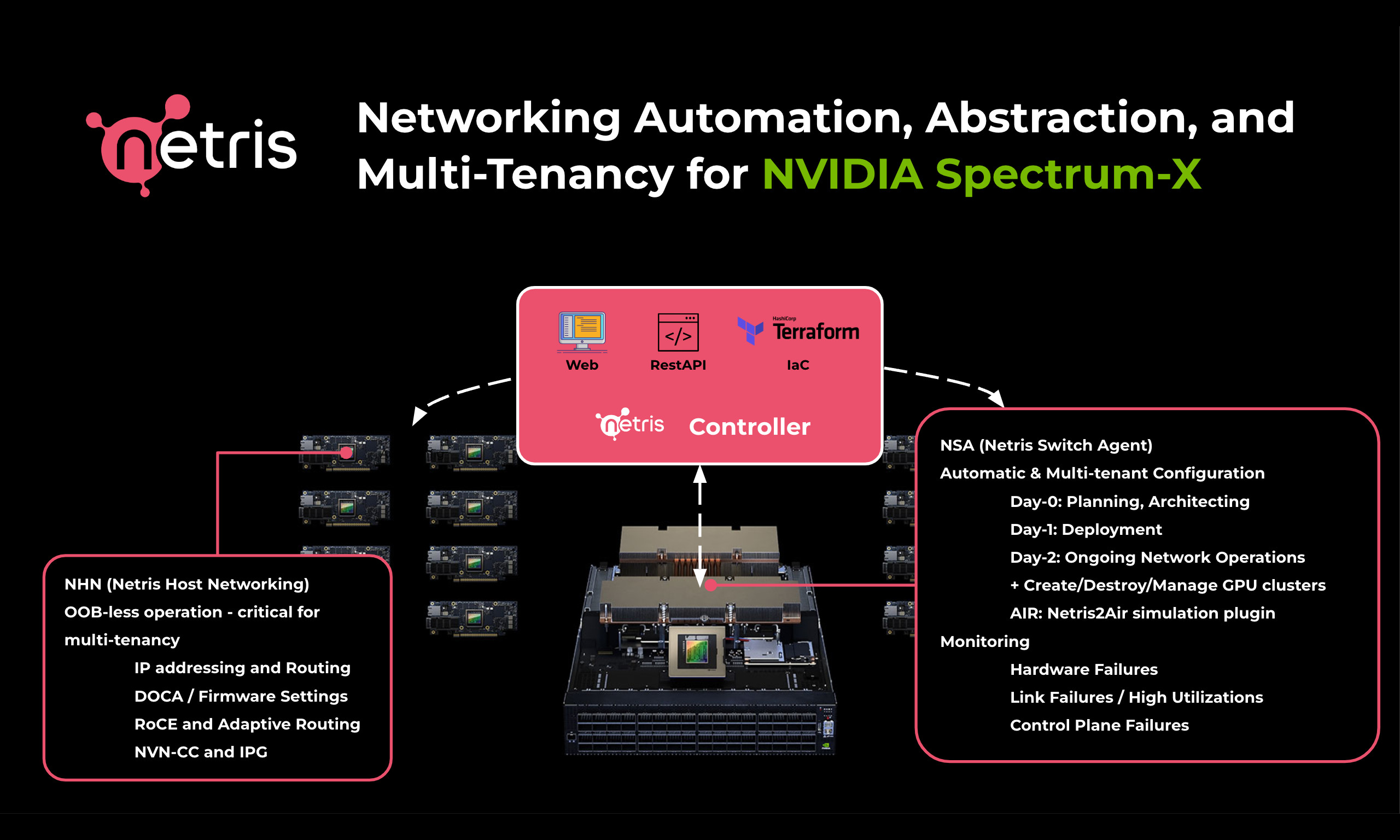
Netris Unveils Networking Automation, Abstraction, and Multi-Tenancy for NVIDIA Spectrum-X
Netris version 4.3.0 has been recently released, enabling a number of functionalities for GPU-based AI cloud providers and operators. Most pieces have been designed to support the NVIDIA Spectrum-X networking platform reference guidelines and factor in best practices and field experience.
The NVIDIA Spectrum-X networking platform, featuring NVIDIA Spectrum-4 switches and NVIDIA BlueField-3 SuperNICs, is the world’s first Ethernet fabric built for AI, accelerating generative AI network performance by 1.6X over traditional Ethernet fabrics. Spectrum-X was developed specifically for GPU-to-GPU connectivity, often referred to as east-west data center traffic.
Many private and public cloud operators have been using Netris in CPU cloud scenarios to achieve network automation, abstraction, and multi-tenancy. These deployments often include NVIDIA Spectrum switches running Cumulus Linux.
It is challenging for a cloud services provider to develop the network automation, abstraction, and multi-tenancy software in-house and deliver typical cloud native constructs such as VPCs, Internet Gateways, NAT Gateways, Elastic IPs, and Elastic Load Balancers.
With Netris, these functionalities are available for CPU cloud providers as well as for GPU cloud providers.
Switch-fabric automation and abstraction with NVIDIA Spectrum-X

Netris switch-fabric management functionality for NVIDIA Spectrum switches is designed to automate the day-0, day-1, and day-2 phases of switch fabric operations.
Day-0:
A Netris controller initialization workflow comes as a Terraform module to help providers generate initial data for Inventory, IPAM, and network topology. The initialization module has knowledge of rail-optimized network topologies for Spectrum-X. It calculates the appropriate number of switches, IP addressing, and rail-optimized topology and creates the necessary blueprints in the Netris controller automatically based on the number of GPU servers.
NVIDIA provides clear guidelines for east-west AI fabrics with Spectrum-X, and Netris software helps users consistently adhere to these standards. However, the north-south fabric offers more flexibility. To accommodate this, the Netris initialization module accepts additional parameters, such as the number of leaf, management, and spine switches, the number of leaf-to-spine links, and various other optional settings. This approach gives users an easy and flexible way to create validated blueprints from day one of network deployment.
Users can also add custom changes to the topology – Netris does not force constraints on topology. It only suggests based on the validated designs.
Day-1:
Netris introduced the Netris2Air plugin, which allows users to leverage the NVIDIA Air networking simulation tool to automatically create a digital twin of the network based on inventory, IPAM, and the topology blueprint declared in the Netris controller. This helps during the design and staging phases to evaluate the resulting network before applying it to the production hardware.
NVIDIA Base Command Manager users can also leverage the integration of BCM and Netris. The BCM built-in ZTP is capable of bootstrapping switches based on MAC addresses defined in the Netris blueprint, binding between a physical network switch and logical switch in the Netris controller, and handing over further automatic management to Netris. This model allows for the use of a single bootstrapping mechanism for both GPU servers and network switches.
Netris supports the parallel management of multiple, physically separate fabrics in a given site. This is critical for cloud providers because GPU-based AI clouds always have multiple switch fabrics.
Netris automatically generates configurations for both east-west and north-south fabrics to bring up the underlay BGP/EVPN fabrics according to the blueprint generated in the Netris controller.
The Spectrum-X fabric, the east-west fabric for AI networking over Ethernet, requires slightly different configurations in order to enable AI-specific functionalities such as QoS, RoCE, Adaptive Routing, Congestion Control, ASIC monitoring, and others. Netris software algorithms know how to handle these AI-specific configurations and are able to distinguish between the Spectrum-X fabric from the North-South fabric to automatically configure both fabrics safely and appropriately.
Monitoring
Basic monitoring features are built in, and Netris will alert users to wiring mismatches, link status errors, or switch health issues. For more comprehensive monitoring, the NVIDIA NetQ network operations toolset can be used alongside Netris, providing deeper insights. Netris is also working on further integrating with NetQ to offer even more detailed analytics and a smoother experience.
NVIDIA InfiniBand Support
A Netris plugin for the NVIDIA UFM network management platform will be available in Netris version 4.4.0, which will be the “glue” between Netris controller and NVIDIA UFM. This functionality is for cloud providers that use Ethernet networking as their TAN (Tenant Access Network) and NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand as their compute network.
Bottom Line
In these examples, by acting as both the fabric manager and the source of truth for the NVIDIA Spectrum-X Ethernet fabric and the NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand fabric (where NVIDIA UFM is the fabric manager), Netris can deliver cloud networking constructs for the entire cluster through a single abstract API.
Host Networking and DPU/SuperNIC
Netris can optionally manage host networking, including dynamic IP address assignments and static route configurations. It also handles various DPU/SuperNIC setups necessary for optimal GPU performance in a Spectrum-X environment. All configurations are managed by Netris software, helping ensure a secure solution for multi-tenant deployments.
Network Isolation & Multi-tenancy
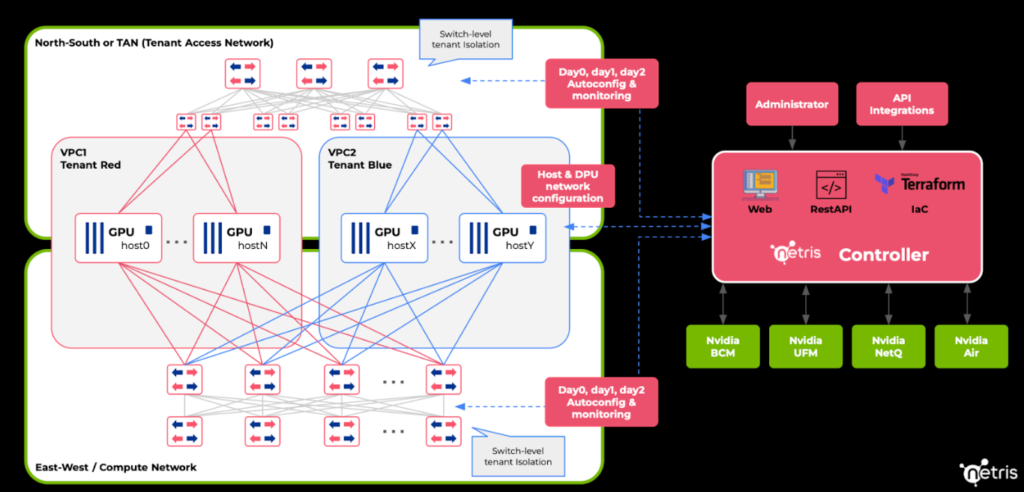
From a GPU-based AI cluster use case perspective, a common operation is to carve out clusters isolated on the network switch level, allowing each tenant to access only resources assigned to them. It is challenging for cloud providers to automate this part in house, even in CPU networks, but it’s more challenging in GPU networks because there are multiple fabrics (East-West, North-South/TAN, OOB-management). Each fabric requires various low-level and different isolation techniques (Layer-2 VXLAN, Layer-3 VXLAN, VRFs, or pKeys).
Netris streamlines network isolation and multi-tenancy for cloud providers. Netris provides simple APIs where the user (or user-facing portal) can request a new “Cluster” and list GPU servers. The user (or user-facing portal) can choose the cluster to be either in a new VPC (Virtual Private Cloud – a unit of isolation in the cloud native world) or in one of the existing VPCs. Such an API request does not need to contain switch-fabric level details – only a simple list of servers – Netris software will figure out and implement the necessary configuration dynamically on the fly – without conflicts – following all NVIDIA Spectrum-X deployment guidelines and best practices.
Once the API request has been submitted to the Netris controller, Netris agents running on every switch and GPU hosts (optional) will automatically reconfigure the network to deliver required access and isolation across VPCs and groups of GPU servers.
All Netris functionality is accessible through (1) a web console – for viewing and ongoing changes, (2) RestAPI – commonly used by cloud services providers to consume Netris API from their customer-facing user portals, and (3) Terraform – usually used by the cloud services providers network and DevOps engineers.
These methods are ideal for cloud providers that would like to offer dynamic multi-tenancy for their customers.
In & Out To/From the AI/GPU cloud – Peering, NAT, Access Control, Direct Connect, and Load Balancing
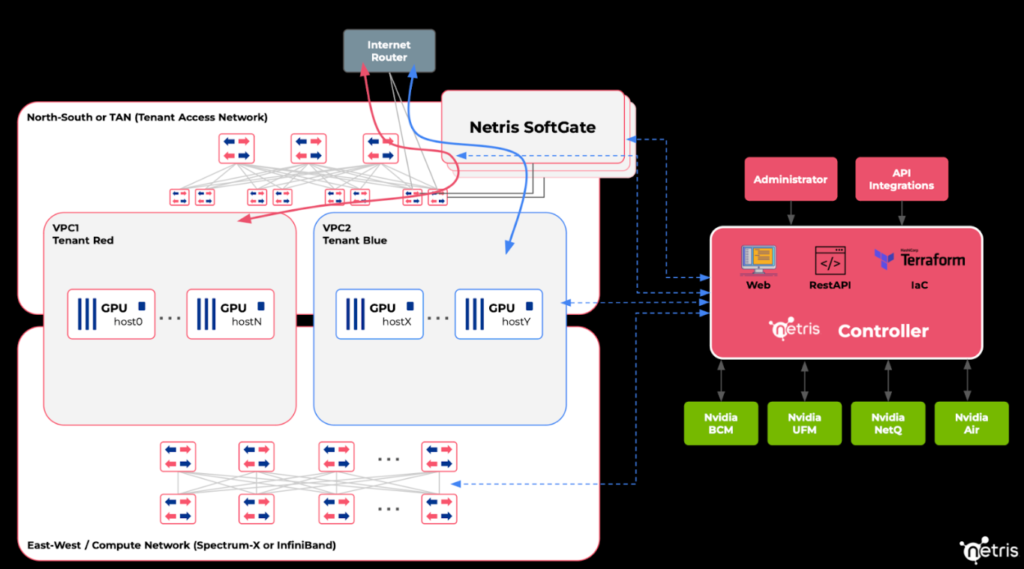
When NCPs (Nvidia Cloud Partners) are building a cloud, they need to mimic cloud networking constructs beyond isolation, VPCs, and multi-tenancy. See, the isolated tenants, VPCs need secure access to/from the Internet and sometimes peering with end users’ other remote networks.
Netris SoftGate HS (hyper-scale) is a software gateway that is designed to utilize regular servers to provide multi-tenant VPC-aware and hyper scalable cloud networking services, such as (1) Internet Gateway – provide Internet access to the hosts in the VPC, (2) NAT Gateway – provide 1:1 NAT, Port-forwarding, or elastic IP services, (3) Elastic Load Balancing – critical for inference workloads to load balance the incoming requests across multiple servers, and (4) Direct connect – to allow a tenant connect their VPC cluster to their remote data center or remote office network.
These cloud networking constructs are essential services that every public cloud provider provides to their users, so when NCPs (Nvidia Cloud Partners) evaluate network automation and abstraction strategies, they should make sure to factor in these critical services.
Ideal for Cloud Providers building Dynamic & Multi-Tenant AI/GPU Clouds.

How to learn more?
- Contact us and schedule a demo meeting.
- Subscribe to our newsletter (at the bottom of the page) and stay informed about updates
- Follow us on LinkedIn and X.




